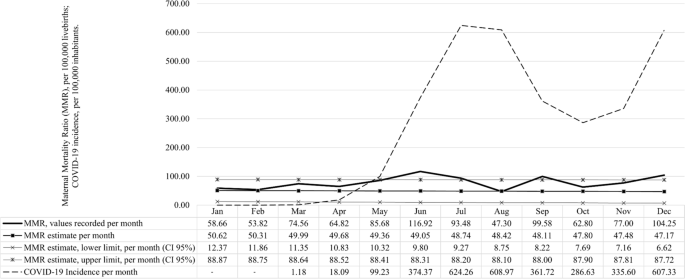
Background Most studies on the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection have been conducted with adults and non-pregnant women. Thus, its impacts on maternal health are not yet fully established. This study aimed to verify the relationship between the maternal mortality ratio and the incidence of COVID-19 in the State of Bahia, Brazil, 2020. Methods This time-series study used publicly available information in Brazil, to obtain data on maternal deaths and live births in Bahia, State, from January 1, 2011, to December 31, 2020. The time trend of Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) was analysed through polynomial regression, of order 6. Expected MMR, monthly (Jan-Dec) and annual values for 2020, were predicted by the additive Holt-Winters exponential smoothing algorithm, with 95% confidence interval, based on the time series of the MMR from 2011 to 2019, and the accuracy of the forecasts for 2020 was assessed by checking the smoothing coefficients and the mean errors. According to the statistical forecast, the MMR values recorded in the year 2020 were compared to those expected. Results In 2020, the annual MMR in Bahia, Brazil, was 78.23/100,000 live births, 59.46% higher than the expected ratio (49.06 [95% CI 38.70–59.90]). The increase in maternal mortality ratio relative to expected values was observed throughout the 2020 months; however, only after May, when the COVID-19 epidemic rose sharply, it exceeded the upper limit of the 95% CI of the monthly prediction. Of the 144 registered maternal deaths in 2020, 19 (13.19%) had COVID-19 mentioned as the cause of death. Conclusions Our study revealed the increase in maternal mortality, and its temporal relationship with the incidence of COVID-19, in Bahia, Brazil, in 2020. The COVID-19 pandemic may be directly and indirectly related to this increase, which needs to be investigated. An urgent public health action is needed to prevent and reduce maternal deaths during this pandemic, in Brazil.

The impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy outcomes in a diverse cohort in England

Maternal mortality linked to COVID-19 in Latin America: Results from a multi-country collaborative database of 447 deaths - ScienceDirect
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic in the Brazilian maternal mortality ratio: A comparative analysis of Neural Networks Autoregression, Holt-Winters exponential smoothing, and Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average models

PDF) OC04.04: Maternal mortality due to COVID‐19 in Brazil

Maternal mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in Mexico: a preliminary analysis during the first year, BMC Public Health

Early estimates of the indirect effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and child mortality in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling study - ScienceDirect
NAE Website - The Future of Remote Monitoring for Pregnancy

Enny Paixao Cruz - Associate Professor - London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, U. of London
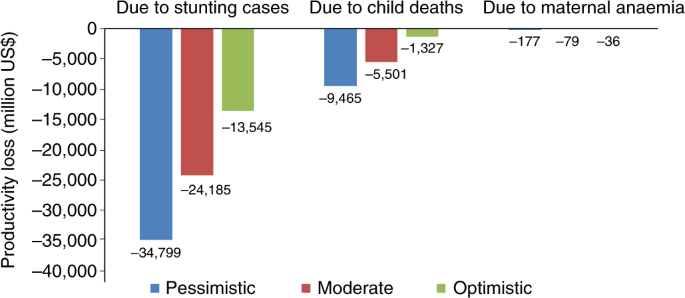
The COVID-19 crisis will exacerbate maternal and child undernutrition and child mortality in low- and middle-income countries
Healthcare utilization and maternal and child mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in 18 low- and middle-income countries: An interrupted time-series analysis with mathematical modeling of administrative data

Covid-19 Shutdowns Disproportionately Harmed Women, Johns Hopkins

Estimation of Basic Reproduction Number and Herd Immunity for COVID-19 in India
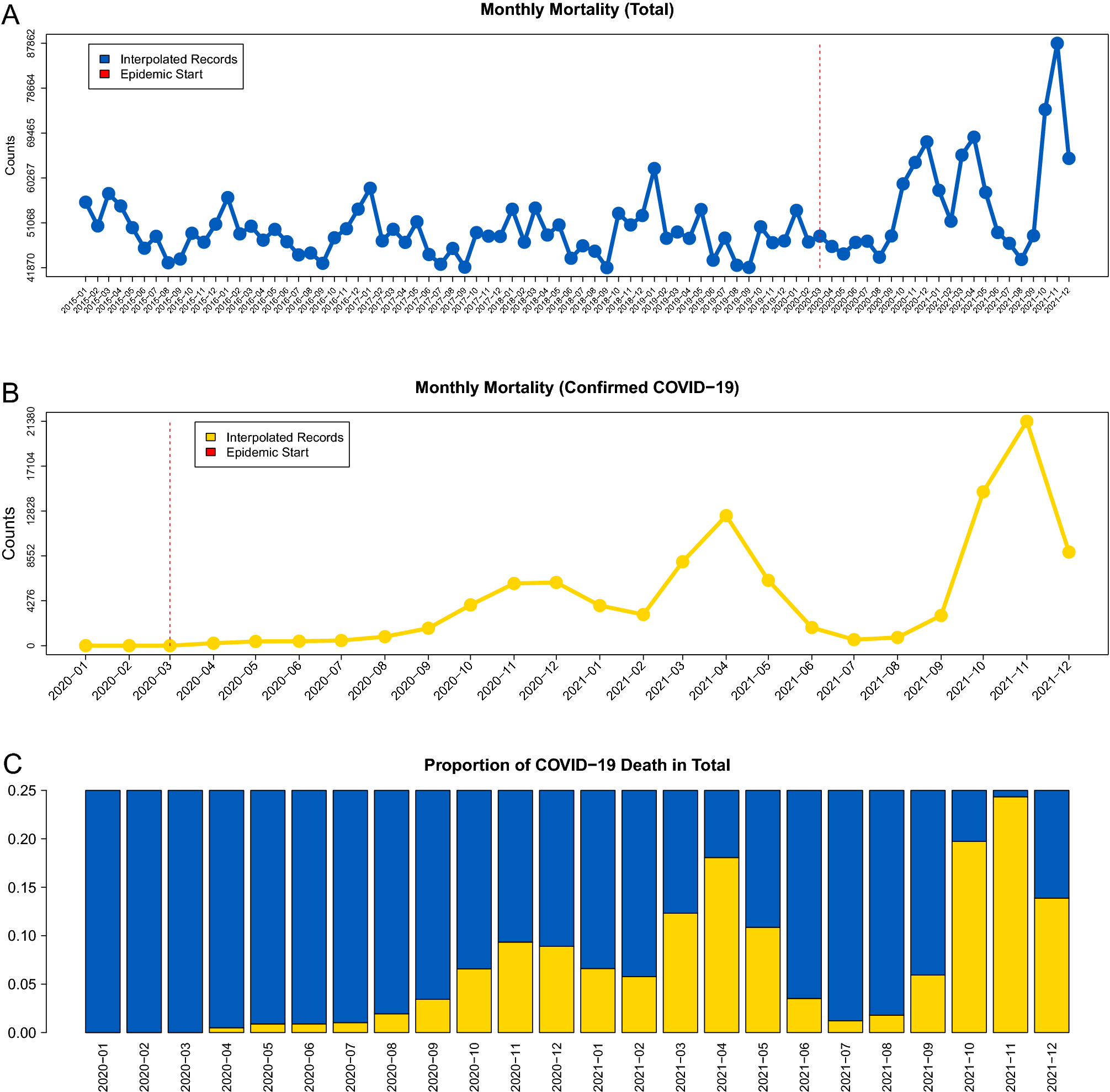
Excess mortality in Ukraine during the course of COVID-19 pandemic in 2020–2021

PDF) Impact of COVID-19 pandemic in the Brazilian maternal mortality ratio: A comparative analysis of Neural Networks Autoregression, Holt-Winters exponential smoothing, and Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average models

The Economic Burden of COVID-19 Infections amongst Health Care Workers



/product/14/7909621/1.jpg?4175)



