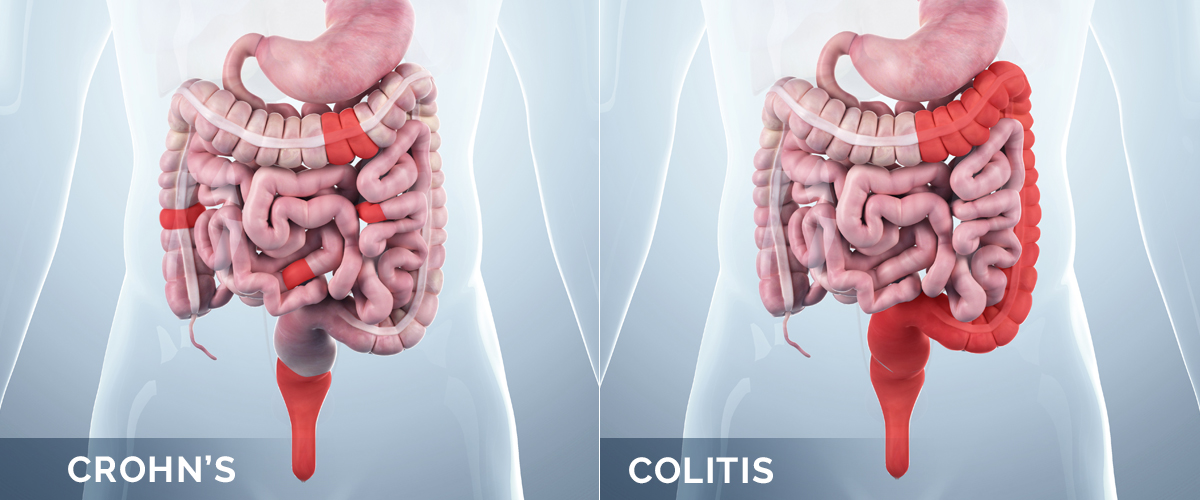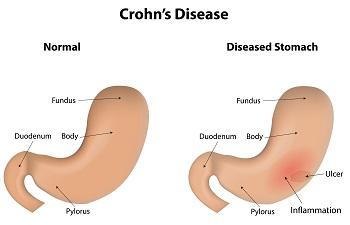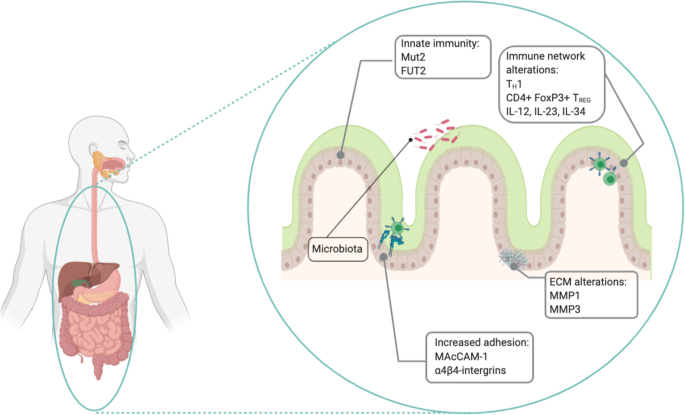
Chron’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disease, first described at the beginning of the last century. The disease is characterized by the alternation of periods of flares and remissions influenced by a complex pathogenesis in which inflammation plays a key role. Crohn’s disease evolution is mediated by a complex alteration of the inflammatory response which is characterized by alterations of the innate immunity of the intestinal mucosa barrier together with a remodeling of the extracellular matrix through the expression of metalloproteins and increased adhesion molecules expression, such as MAcCAM-1. This reshaped microenvironment enhances leucocytes migration in the sites of inflammation, promoting a TH1 response, through the production of cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α. IL-12 itself and IL-23 have been targeted for the medical treatment of CD. Giving the limited success of medical therapies, the treatment of the disease is invariably surgical. This review will highlight the role of inflammation in CD and describe the surgical approaches for the prevention of the almost inevitable recurrence.

Endoscopic imaging in inflammatory bowel disease
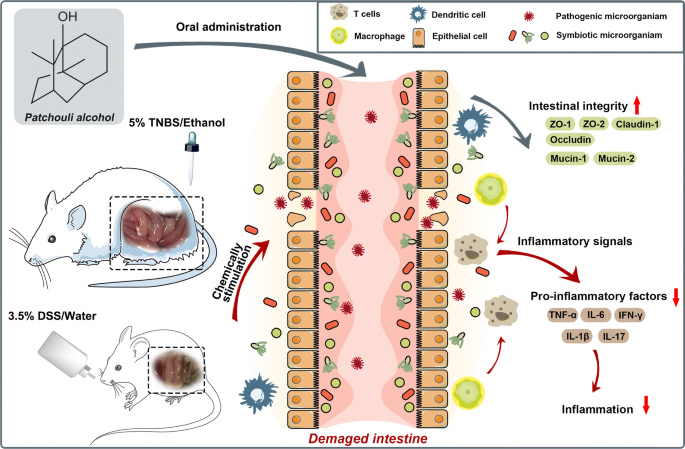
Patchouli Alcohol: a Natural Sesquiterpene Against Both Inflammation and Intestinal Barrier Damage of Ulcerative Colitis

Full article: Detailed immune profiling in pediatric Crohn's disease using methylation cytometry

PDF] Ulcerative colitis: Recent advances in the understanding of disease pathogenesis

Crohns Disease, PDF, Crohn's Disease

Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease.
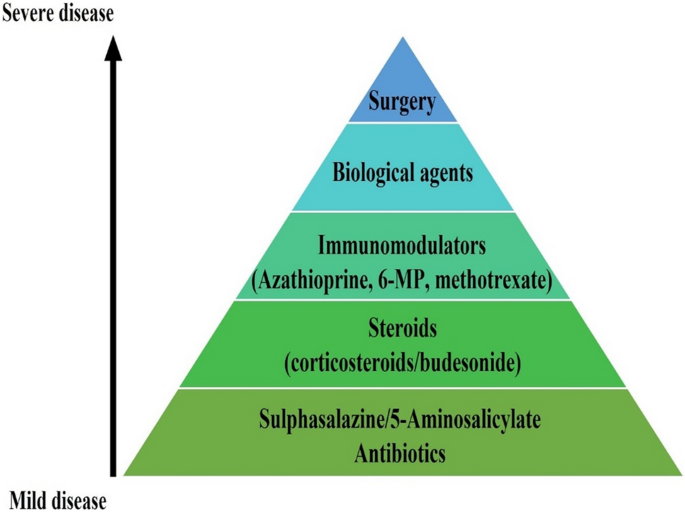
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Disease Modeling
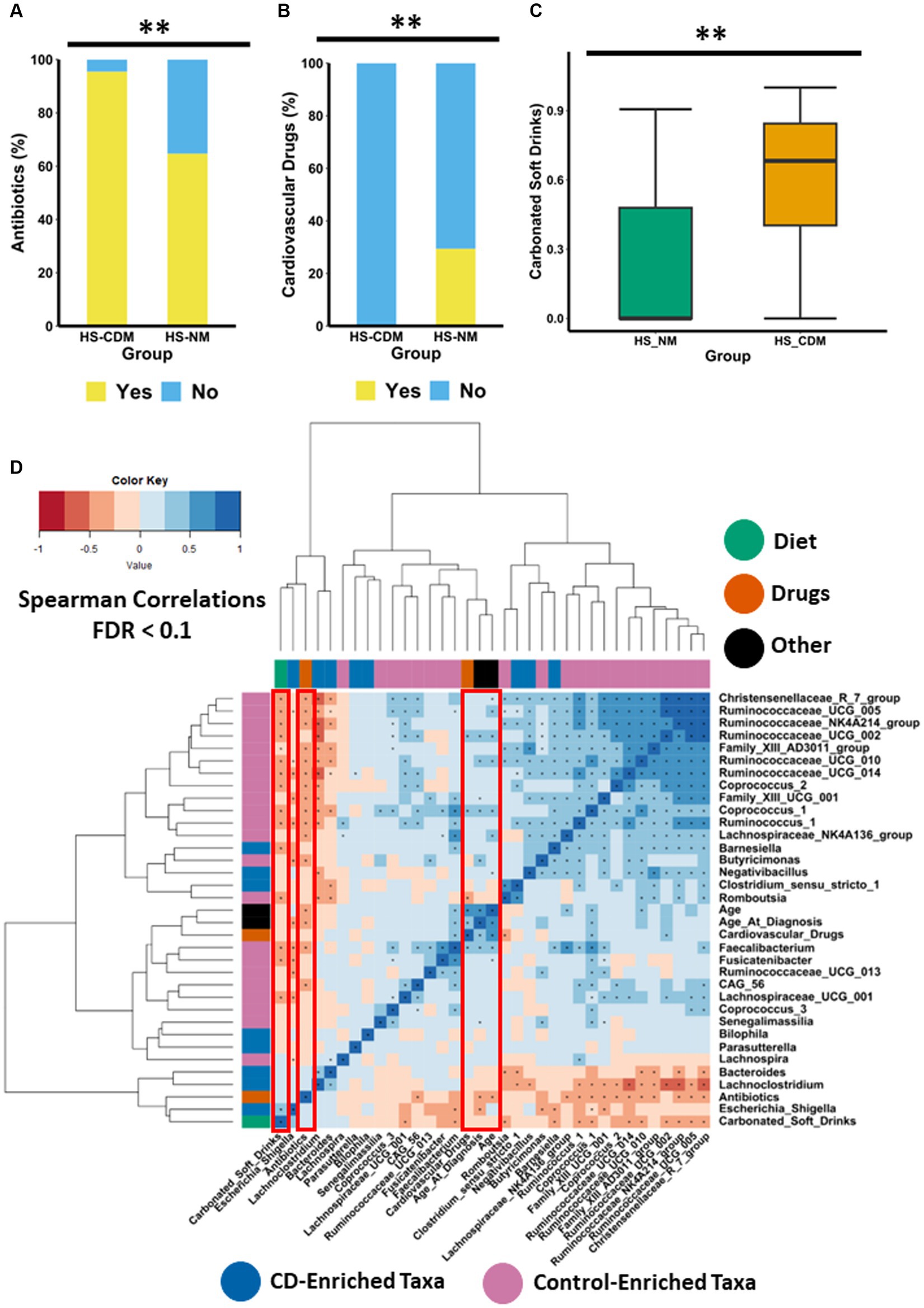
Frontiers Comparative diet-gut microbiome analysis in Crohn's disease and Hidradenitis suppurativa
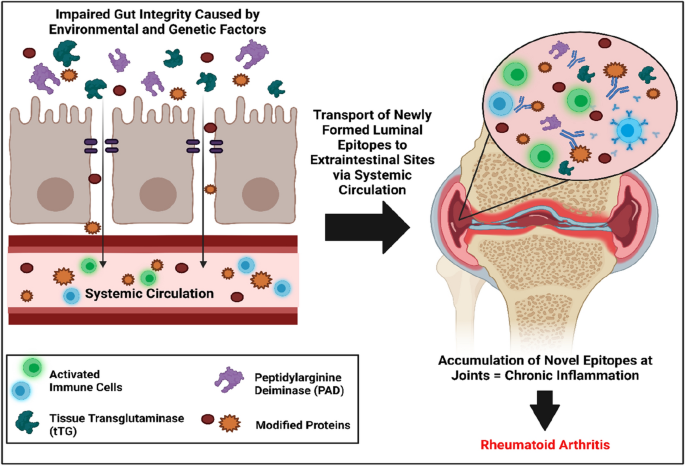
Increased Intestinal Permeability: An Avenue for the Development of Autoimmune Disease?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Types-of-Crohns-Disease-Surgeries_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-9f456387121a479094f62d33591df9e9.jpg)