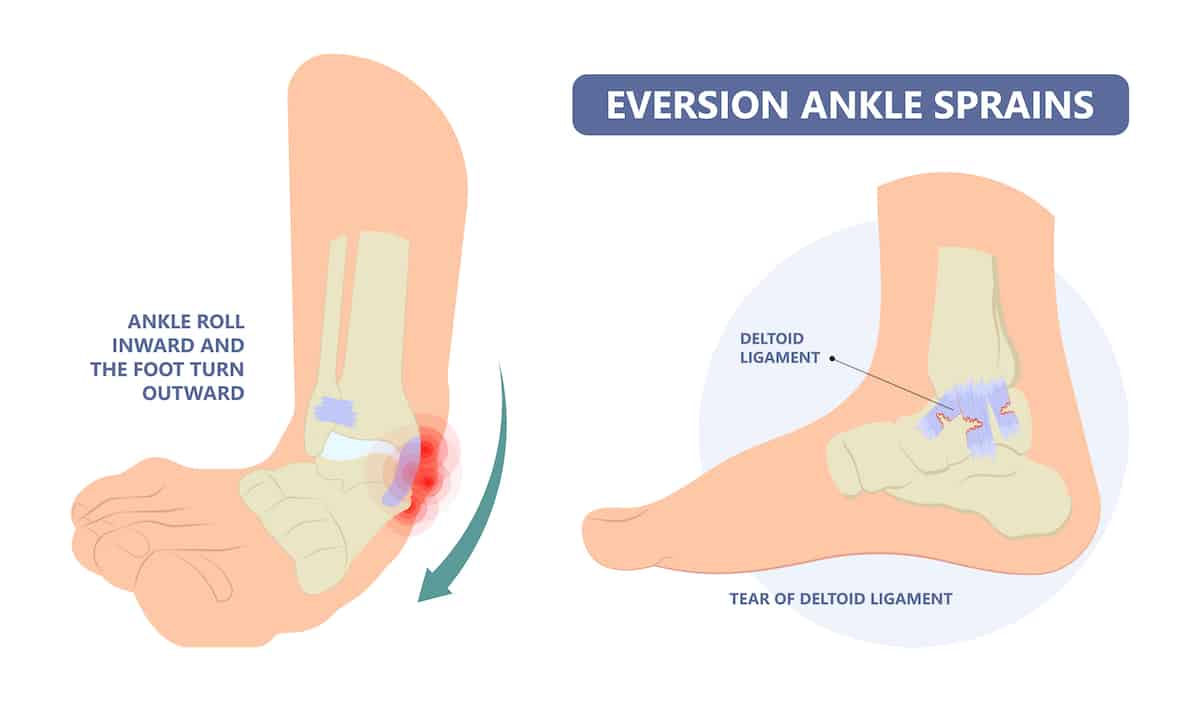
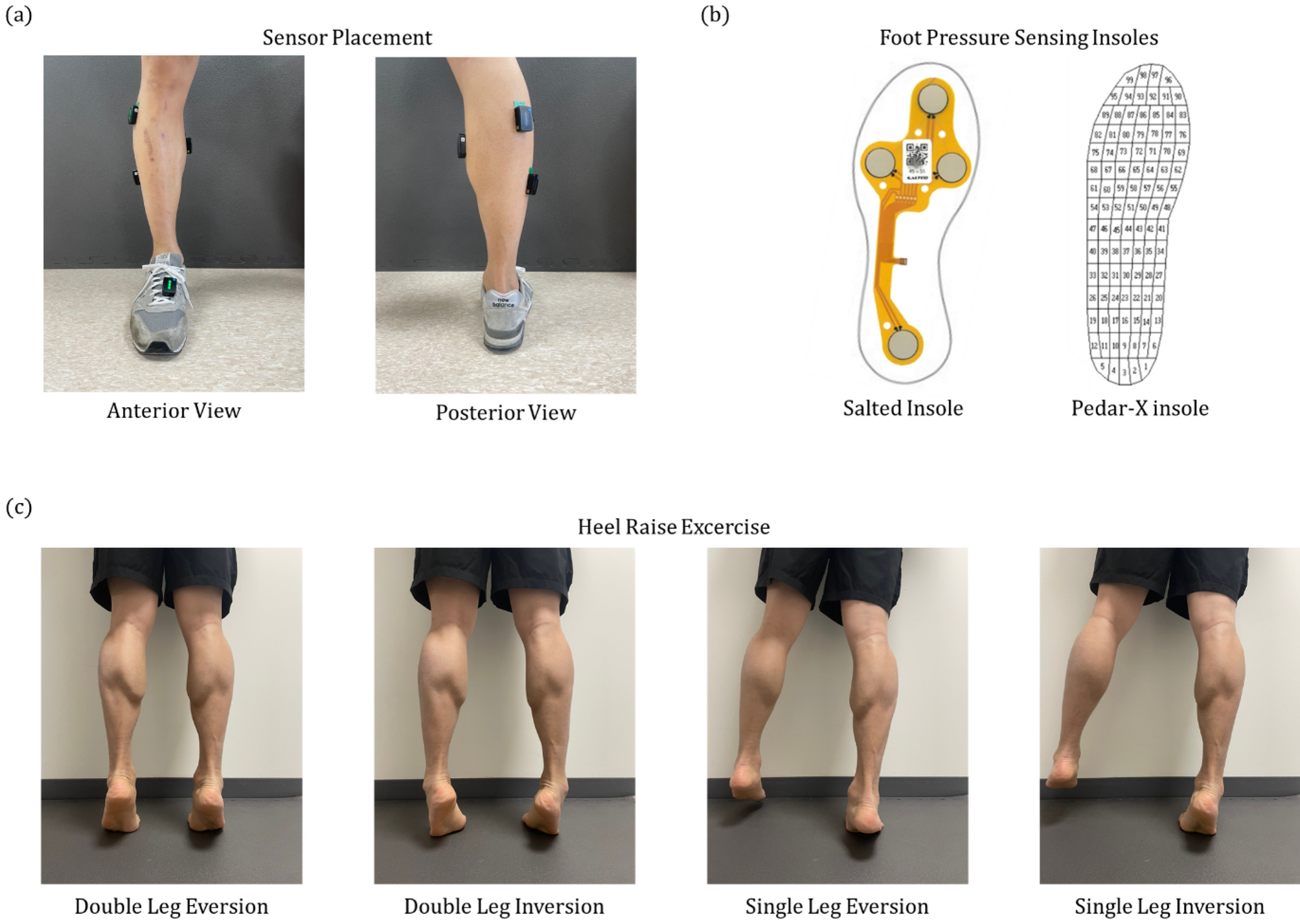
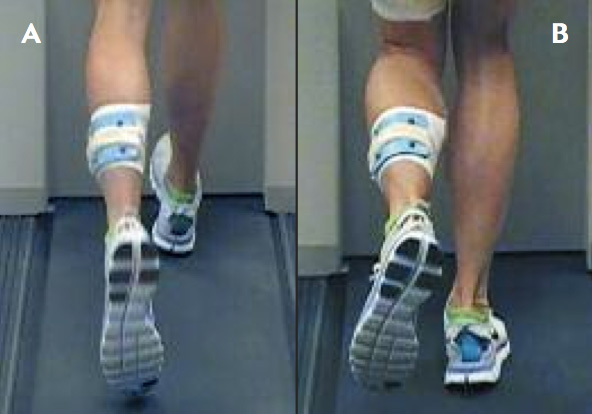
Download scientific diagram | — Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire gait cy- cle, there was a significant mean difference of 2.07 ° ± 0.29 ° between chronic-ankle-insta- bility (CAI) and control subjects. CAI subjects demonstrated more inversion than controls. from publication: Altered Ankle Kinematics and Shank-Rear-Foot Coupling in Those With Chronic Ankle Instability | Kinematic patterns during gait have not been extensively studied in relation to chronic ankle instability (CAI). To determine whether individuals with CAI demonstrate altered ankle kinematics and shank-rear-foot coupling compared with controls during walking and jogging. Case | Ankle Joint, Kinematics and Gait | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
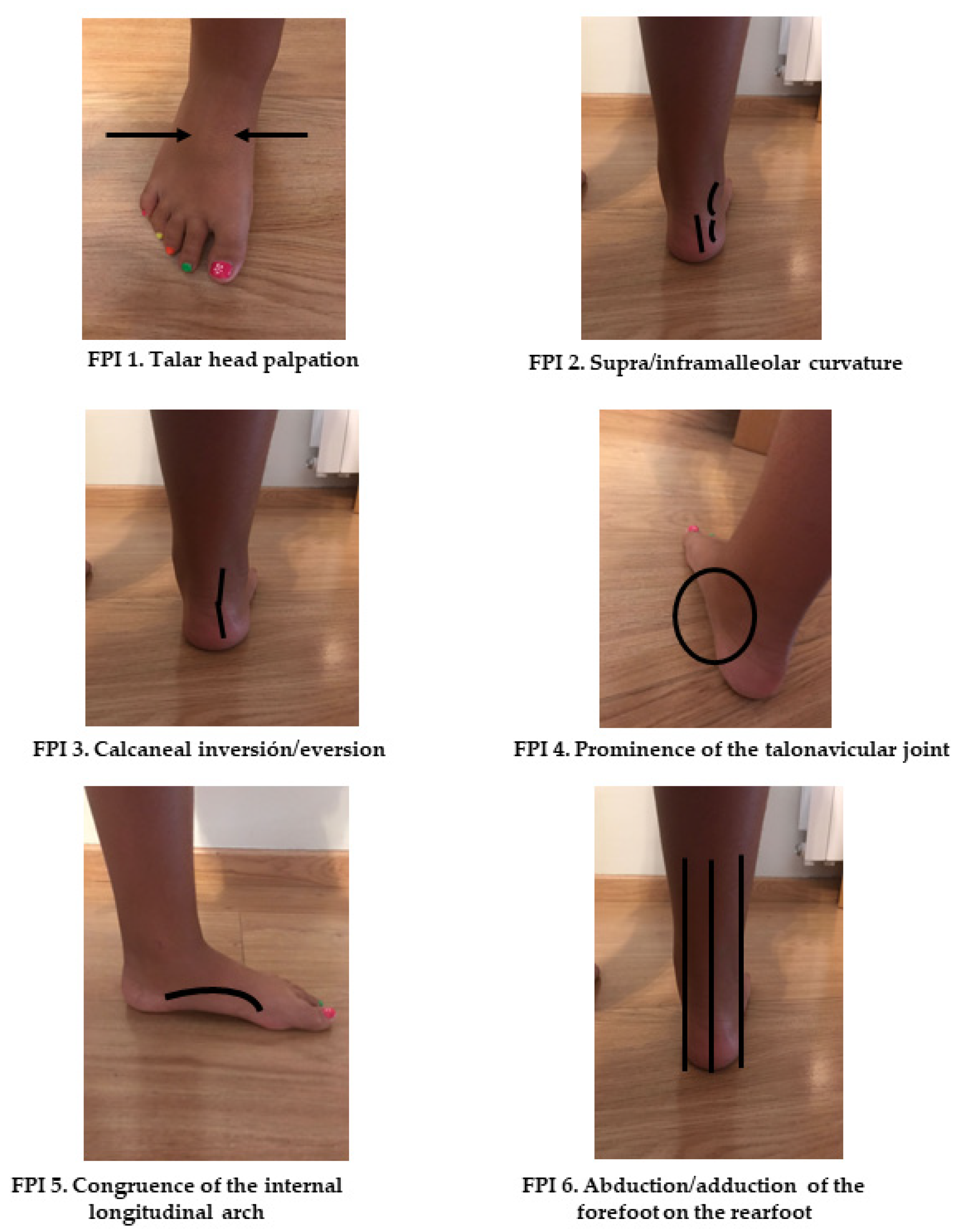
Children, Free Full-Text

D. KERRIGAN, Research and Development

PDF) Altered Ankle Kinematics and Shank-Rear-Foot Coupling in Those With Chronic Ankle Instability

Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire

Orthotics for Common Foot Ailments - Pronation & Supination

PDF) Altered Ankle Kinematics and Shank-Rear-Foot Coupling in Those With Chronic Ankle Instability

Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire
Simulating the effect of ankle plantarflexion and inversion-eversion exoskeleton torques on center of mass kinematics during walking
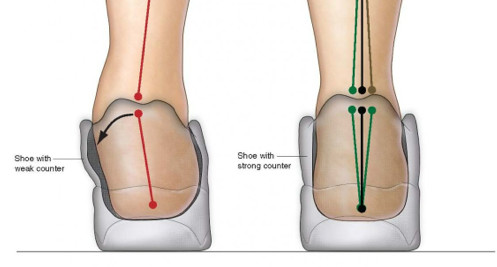
What Is Foot Pronation And Foot Supination? Is It Good Or Bad?

Different foot orthosis angles on walking kinematics

The effect of changing mediolateral center of pressure on rearfoot eversion during treadmill running - ScienceDirect

Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire

Midfoot & Rearfoot Conditions Melbourne
Pronation in runners: Implications for injury

Simulating the effect of ankle plantarflexion and inversion-eversion exoskeleton torques on center of mass kinematics during walking