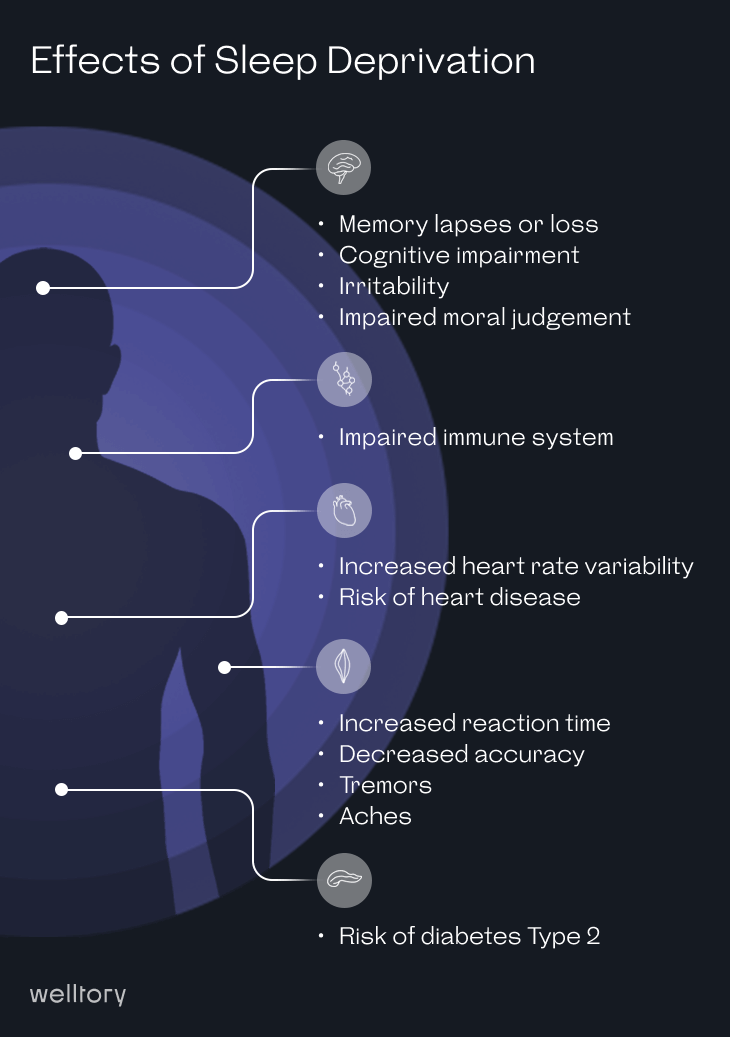
To better understand how the brain protects itself from outside influences, researchers invited 18 participants to a morning nap in the lab.

PSYCH 202 - UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 10 READING NOTES Flashcards

The mysteries of sleep: everything we don't know about why we snooze - BBC Science Focus Magazine

The Sleeping Brain Suppresses External Inputs When Dreaming, But Not During All Sleep

Brain mechanisms of insomnia: new perspectives on causes and consequences

Sleep and the price of plasticity: from synaptic and cellular homeostasis to memory consolidation and integration. - Abstract - Europe PMC

PDF) Brain Reactivity Differentiates Subjects with High and Low Dream Recall Frequencies during Both Sleep and Wakefulness

Sleep and Dreaming

How the Dreaming Brain Suppresses the Outside World
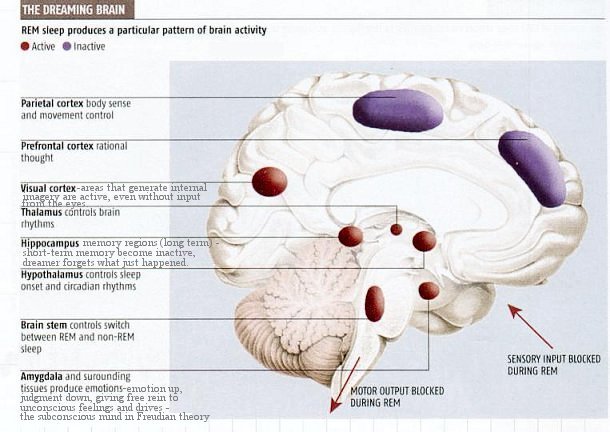
Mulitcellular Organisms
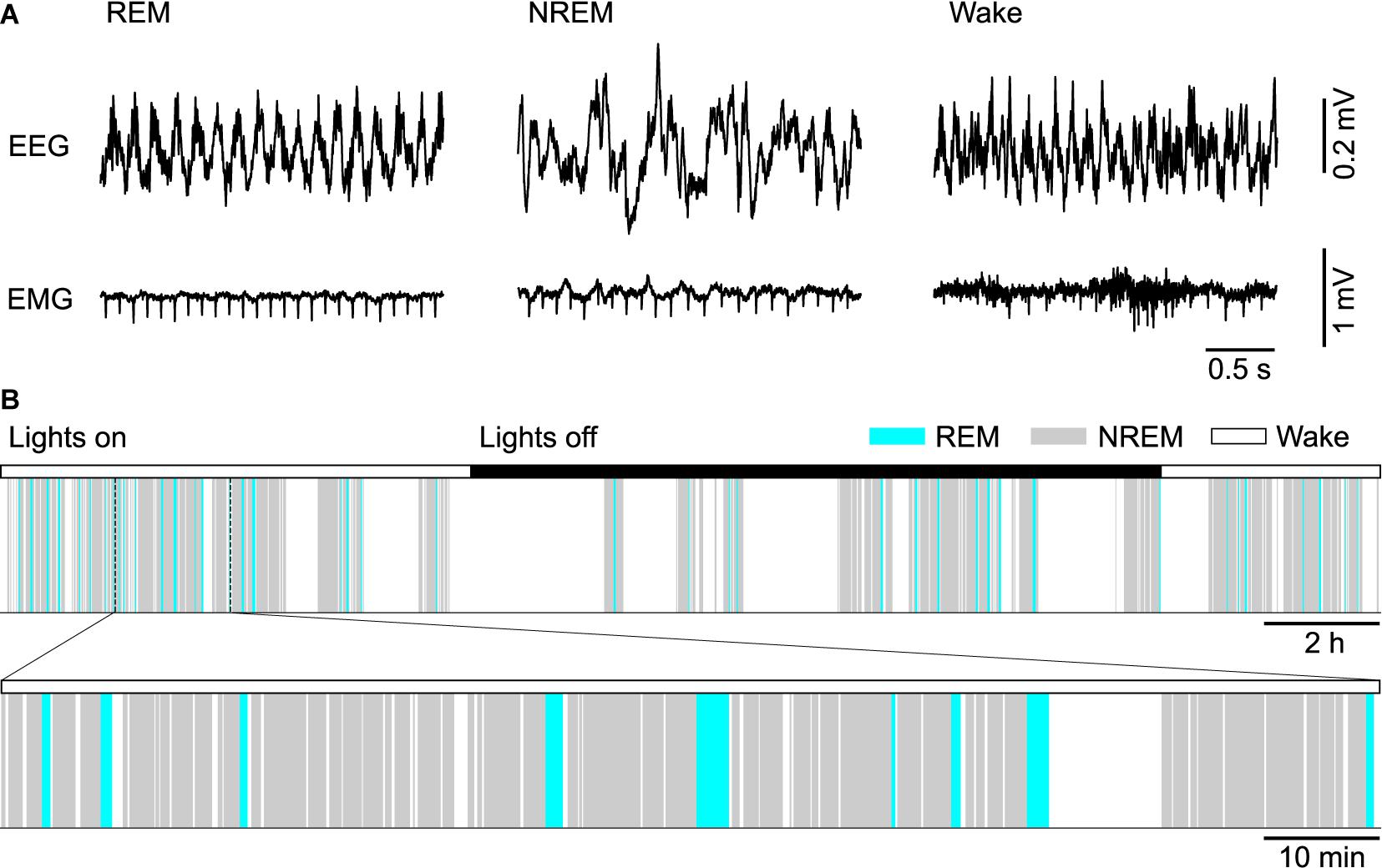
Frontiers Neural and Homeostatic Regulation of REM Sleep
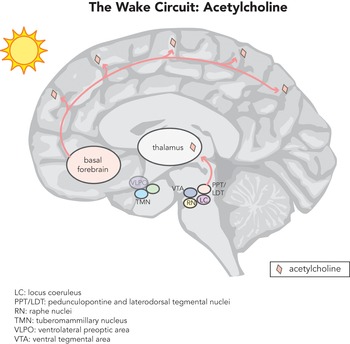
Sleep (Part I) - The Neuroscience of Sleep and Dreams
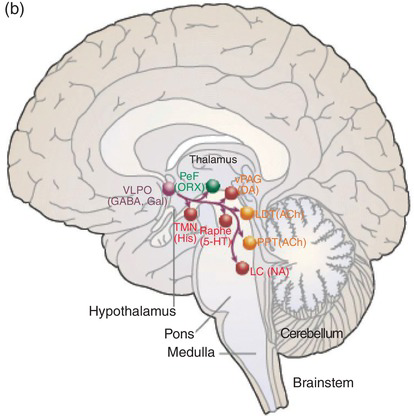
Disorders of Sleep and Wakefulness and Their Treatment: Neurotransmitter Networks for Histamine and Orexin (Chapter 10) - Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology

The Activation-Input Source-Neuromodulation model (AIM). Illustration

PDF) Sleepers Selectively Suppress Informative Inputs during Rapid Eye Movements

Sleep: The Sensory Disconnection of Dreams - ScienceDirect