In this article, we study the influence of the heat transfer coefficient on the heat retention rate per unit length of a wall made of concrete attached to the tow-plaster. The study is done in frequency dynamic regime established conditions. For different values of the exciting pulse, we evaluate the thermal inertia of the wall. The wall has a length of 0.1m including 0.05m of concrete and 0.05m thermal insulating plaster-tow. The thermal conductivity of concrete is about 10 times greater than that of the tow-plaster material. The results show that the thermal behavior of the wall depends partly outdoor climatic constraints. The duration of the outdoor climatic stresses related to the excitation pulse is an important factor on the thermal inertia of the wall. The thermal inertia of the wall is also dependent on the heat exchange coefficient on the surface of the material, its thermophysical properties and initial temperature of the material.

Coatings, Free Full-Text
PDF) Analysis of the effectiveness of thermal insulation of a

Heating ventilation and air conditioning engineering and design Pages 151-200 - Flip PDF Download

Fire performance of non‐load‐bearing double‐stud light steel frame walls: Experimental tests, numerical simulation, and simplified method - Alves - 2022 - Fire and Materials - Wiley Online Library

Soundproofing vs Sound Absorbing – Explaining the Difference

PDF) Influence of Thermal Exchange Coefficient on the Heat
How to calculate the heat loss through a building wall - Quora

Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Fundamentals of heat transfer lecture notes

Thermal insulation solutions for opaque envelope of low-energy
Building Guidelines, Part L 2022

Thermal insulation solutions for opaque envelope of low-energy

PDF) Influence of Thermal Exchange Coefficient on the Heat

PDF) Influence of Heat Exchange Coefficients on Both Optimized
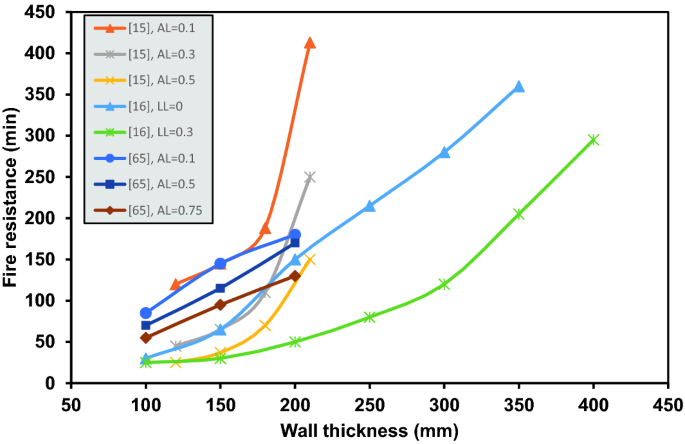
Behaviour of Reinforced Concrete Walls Under Fire: A Review







