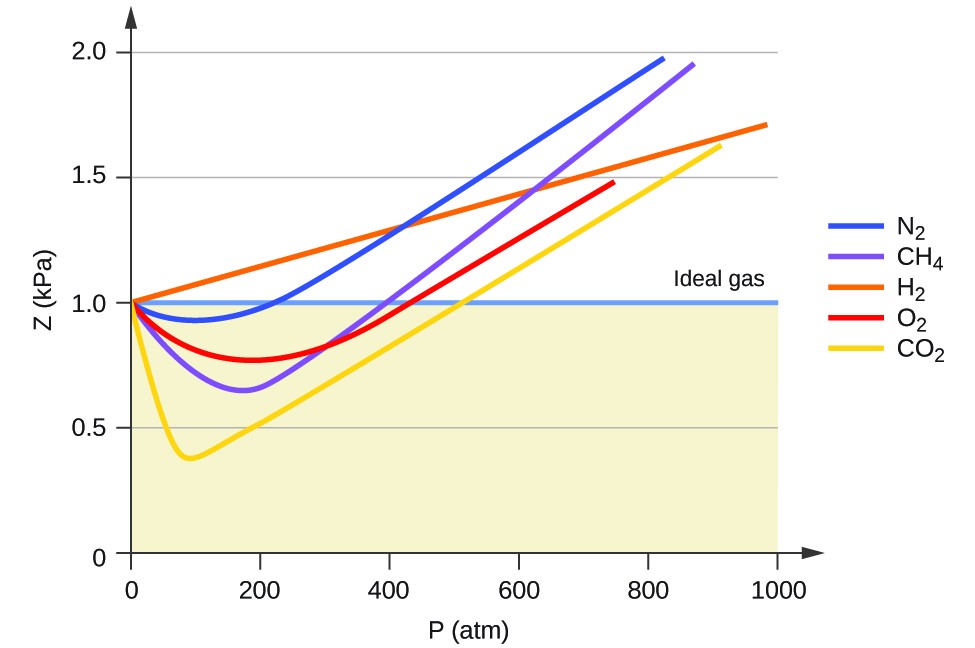
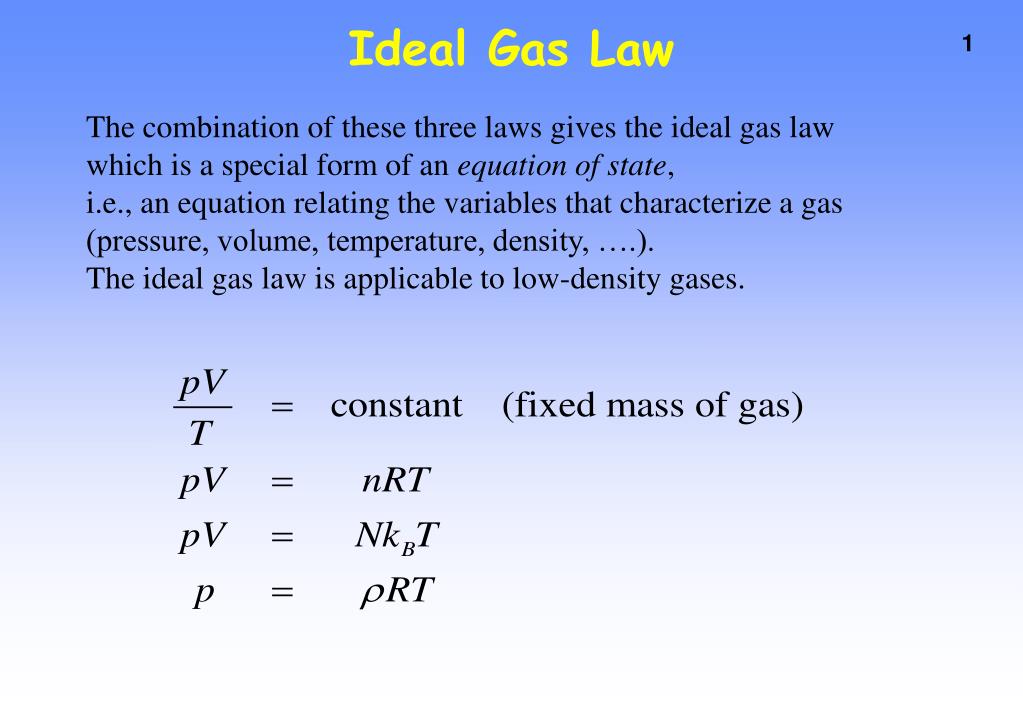
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the …
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the gas constant. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal gas, a hypothetical substance whose behavior can be explained quantitatively by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 0°C and 1 atm.

Foods, Free Full-Text
1. An unspecified ideal gas at 10°C and 100kPa occupies a volume of 2.5 m³. (a) How many moles does this gas have? (b) If the pressure and temperature are raised three

8.1 Chemical Equations and Stochiometric Relationships – Chemistry Fundamentals
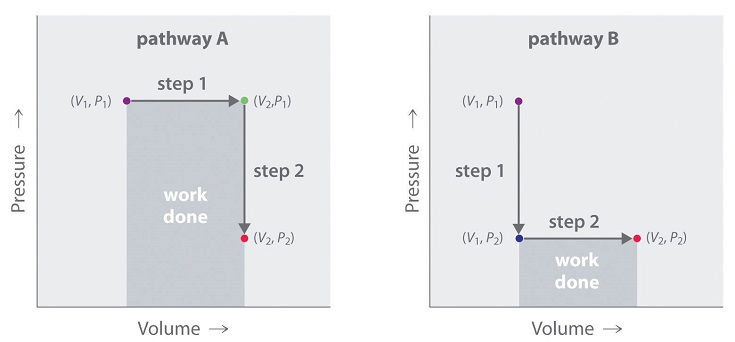
10.4: Quantifying Heat and Work - Chemistry LibreTexts
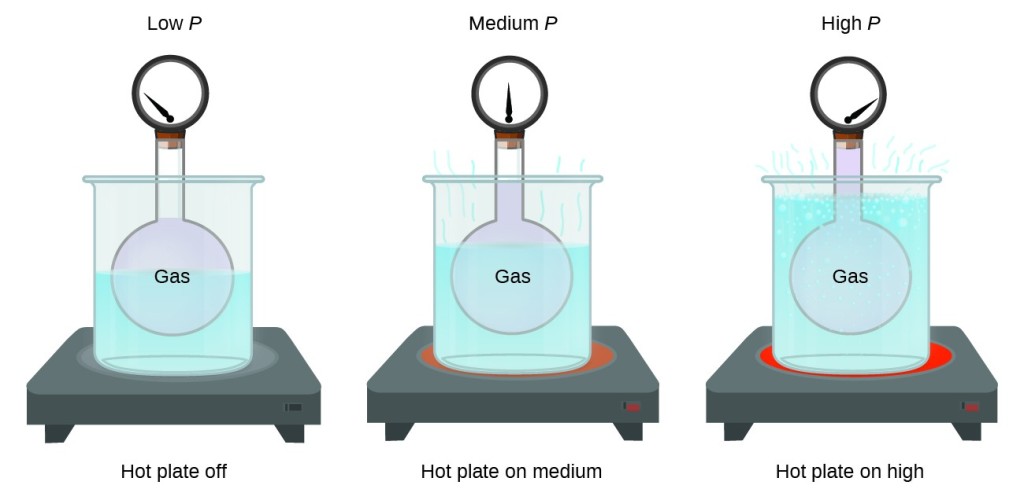
10.3: Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature- The Ideal Gas Law - Chemistry LibreTexts

LibreTexts Textmap of McQuarrie and Simon's Book (Cap 01 - 10) - Química Analítica I
Slides27
What volume will 2.5mol of a gas occupy at 283K and at a pressure of 300torr under ideal conditions? (He also says 3 significant digits and ' (R=62.36L * torr/ (mol *
What volume will 2.5mol of a gas occupy at 283K and at a pressure of 300torr under ideal conditions? (He also says 3 significant digits and ' (R=62.36L * torr/ (mol *
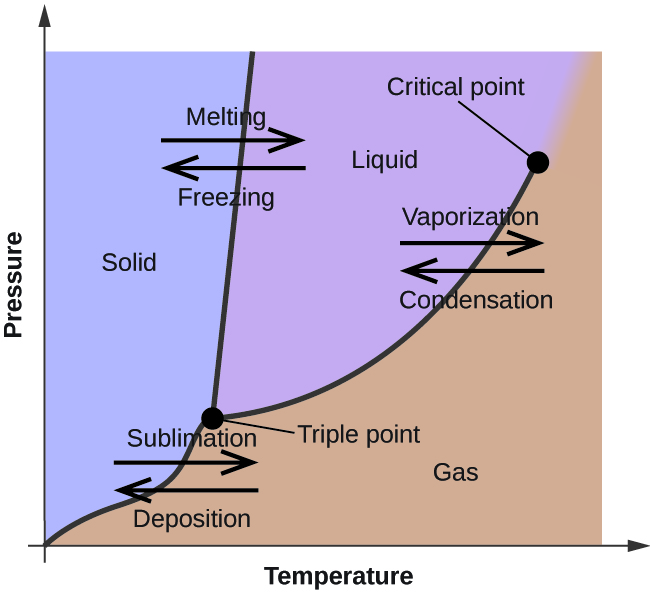
11.5 Phase Diagrams – Chemistry Fundamentals

7.5 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals – Chemistry Fundamentals